Mole Removal
A mole that grows, itches, or changes in any way could be skin cancer. Some people are even trying DIY surgeries, such as removing a mole or skin tag.
Doctors caution that at-home surgery can go seriously wrong quickly and unexpectedly. Trying to remove a mole or skin tag at home could cause a deep-seated infection. You could cause unstoppable blood loss. To get life-saving care, you’d have to go to the emergency room.
Melanoma and skin cancer tests are performed in mole removal procedures. treatment succesfully rate is high with early diagnosis.
Your doctor can identify moles by looking at your skin. You may choose to make a skin examination a regular part of your preventive medical care. If your doctor suspects that a mole may be cancerous, he or she may take a tissue sample (biopsy) for microscopic examination.
Mole removal
If your mole is cancerous, your doctor will do a surgical procedure to remove it. This procedure can also be used for cosmetic reasons.
Mole removal takes only a short time and is usually done on an outpatient basis. Your doctor numbs the area around the mole and cuts it out, along with a margin of healthy skin if necessary. The procedure may leave a permanent scar.
**If you notice that a mole has grown back, see your doctor promptly.**


Doktorunuz muhtemelen size aşağıdakiler gibi bir dizi soru soracaktır:
- When did you first notice this mole?
- Have you always had it, or is it new?
- Have you noticed any changes in this mole, such as its color or shape?
- Have you had other moles surgically removed in the past? If so, do you know if they were unusual (atypical) or malignant?
- Do you have a family history of atypical moles, melanoma or other cancers?
- Have you had peeling sunburns or frequent exposure to ultraviolet radiation, such as from tanning beds?
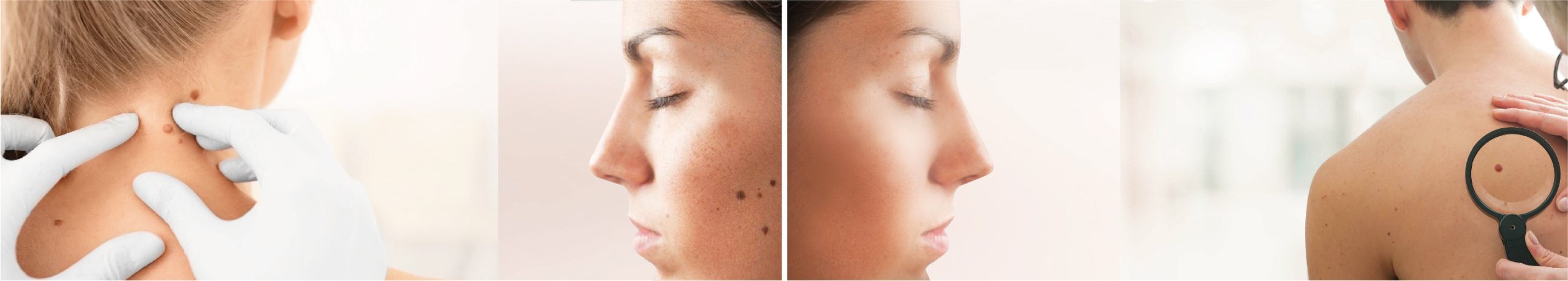
How is a mole removed?
Depending on the size, location and shape, moles may be removed in a number of ways.
Cutting – With smaller nevi, the growth is cut or ‘shaved’ off flush with the skin with a scalpel or surgical scissors,while larger moles may require cutting out and stitching of wound edges.
Freezing- A mole may also be removed with liquid nitrogen. The doctor sprays a small amount of ultra-cold liquid nitrogen on a mole or skin tag, causing a small blister to form. When it heals, the mole will be gone.
Burning – Moles or skin tags may be burned off using an electric current passing through a hot wire. The area is first numbed with an anesthetic and the heat itself helps prevent any bleeding. Freezing and burning do not normally leave scars or marks.
How long will the treatment take?
Unless it is very large, a single mole can usually be removed with an simple incision operation. Several moles or a very large mole may require a series of operations.
What should you expect afterwards?
Normally, once a mole is removed it will not return. If, however, the mole grows back immediately, make a return appointment with your doctor, as this could be a sign of melanoma.
What are the risks of mole removal?
The surgical wound may bleed a little. It will be covered with a dressing and you may have stitches to help keep it closed. The surgical wound could develop an infection, which can usually be treated with antibiotics. Signs of an infection could include redness and swelling